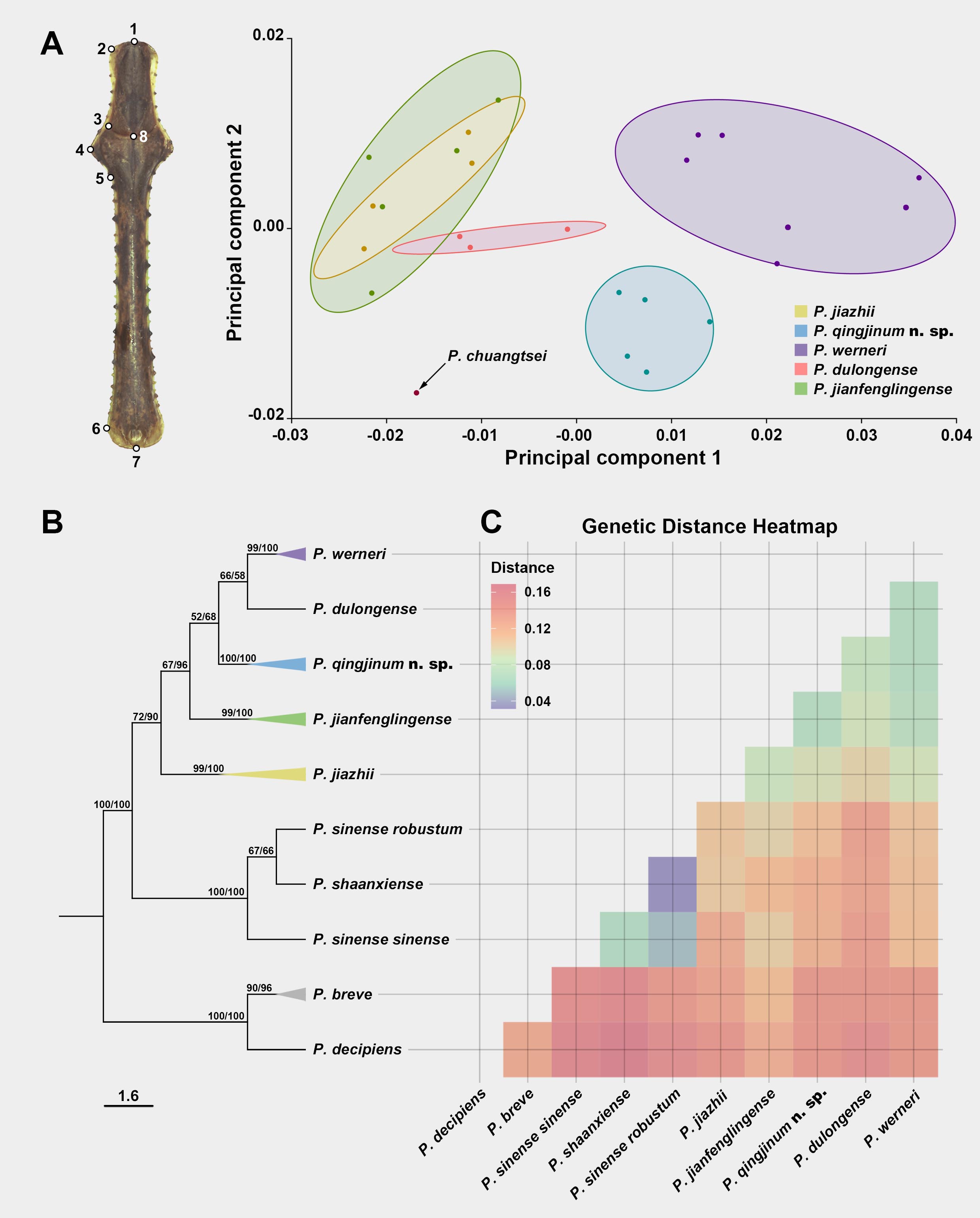
Morphological and molecular divergence of P. qingjinum sp. nov. relative to other species in the P. werneri group. A. Eight morphological landmarks on the pronotum used for Principal Component Analysis (PCA) (the left) and the resulting pronotum shape differences amongst species shown on the right, with circles are 80%-equal frequency ellipses of each species. B. Phylogenetic relationships within the P. werneri group, constructed using IQ-TREE and MrBayes, feature a cladogram-based framework from IQ-TREE, with branches of multiple samples from the same species collapsed into coloured triangles. Node support values are noted directly beside each node, formatted as Bootstrap value/Bayesian posterior probability (%). C. Heatmap illustrates pairwise genetic distances between species under K2P model, where the intensity of the colour reflects the degree of genetic distance, with deeper reds indicating greater genetic divergence.